Hopefully, you have found ducts which identify this as an exocrine gland, composed of many serous acini (with acidophilic secretory granules) and with conspicuous large ducts in the interlobular connective tissue. If you haven't recognized acini and ducts, look again now. (Make sure you distinguish ducts from blood vessels; the ducts are the ones with the cuboidal-to-columnar epithelium, two-layered in the larger examples.)
If you are unnaturally careful and astute, you might also have noticed that some acini have prominent oval nuclei in their centers, with these nuclei appearing similar to those of duct epithelium. (What might you name cells found in the centers of acini?)
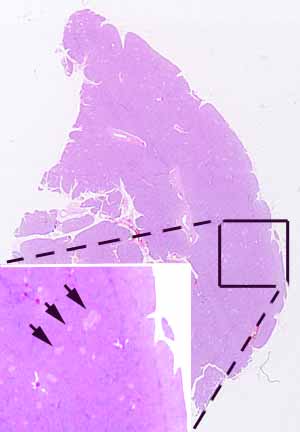
Hopefully, you have also noticed numerous pale patches of cells (e.g., arrows in inset) scattered throughout the parenchyma, and noticed that the cells comprising such patches are organized into cords (resembling parathyroid) rather than acini. If not, please examine the specimen again.
Make sure you can distinguish between the secretory parenchyma and the numerous small intralobular ducts. (In small ducts, the nuclei are centrally located and the cytoplasm is not conspicuously polarized.)
Note the number and location of adipocytes in this specimen. (Trivia: Fat cells are common in intralobular stroma of salivary glands but rare in normal pancreas.)
No more hints.
