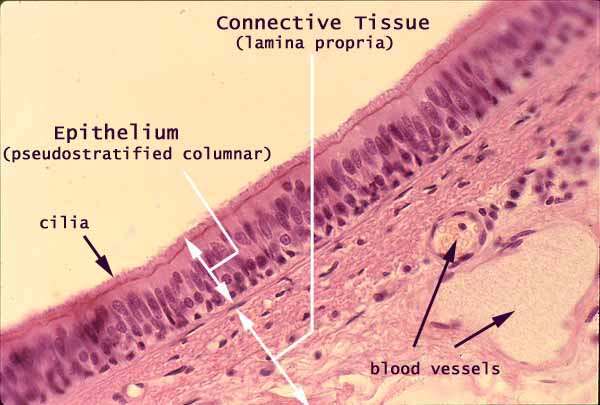

Trachea, epithelium and connective tissue

Pseudostratified columnar epithelium lines the mucosa of the trachea. This epithelium consists of both short and tall cells, all resting on the basement membrane.
Most of the tall (columnar) cells are ciliated, a specialization that allows dust and mucous to be swept upward and eliminated.
The tracheal epithelium is supported by loose connective tissue.
The loose connective tissue of a mucosa is called lamina propria, and typically has a fairly high proportion of cells with immune function.
The small round nuclei may belong to lymphocytes. The more elongated nuclei are most likely fibroblasts.
SIUC / School
of Medicine / Anatomy / David
King
https://histology.siu.edu/intro/CR006c.htm
Last updated: 8 June 2022 / dgk