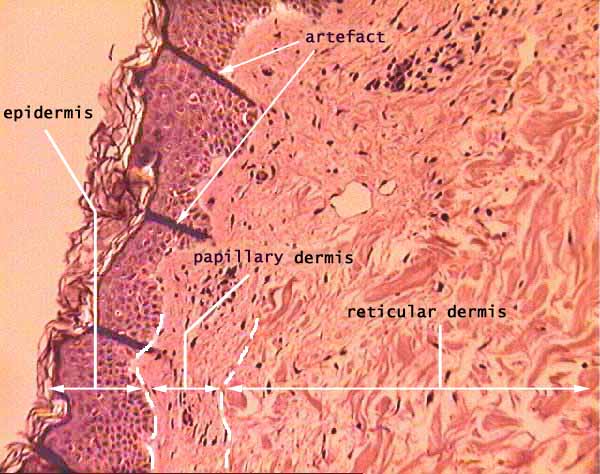

Skin, dermis and epidermis

This image emphasizes the fibrous connective tissue that comprises the dermis.
Although the difference between the finely-textured collagen of the papillary layer and the coarser collagen fibers of the reticular layer can be fairly distinct, as shown here, the boundary between these two dermal "layers" is fairly arbitrary.
In this H&E stained specimen, collagen appears pink while ground substance is unstained (i.e., the pale background color).
The very dark purple (nearly black) spots are cell nuclei. In this location, most of the nuclei belong to fibroblasts. Some may also belong to macrophages, mast cells, or capillary endothelial cells.
Epidermis at left separates the dermis from the outside world. This stratified squamous epithelium consists primarily of keratinocytes.
The dark bars across the epidermis (labelled "artefact" on this image) are wrinkles in the section.
Comments and questions: dgking@siu.edu
SIUC / School
of Medicine / Anatomy / David
King
https://histology.siu.edu/intro/IN033b.htm
Last updated: 12 June 2022 / dgk