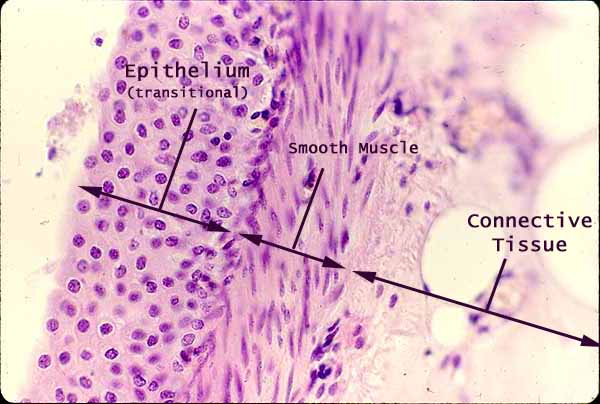

Urinary Tract, epithelium and connective tissue

Transitional epithelium and loose connective tissue comprise the mucosa of the urinary tract.
A transitional epithelium superficially resembles a nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium. But note that the epithelial cells nearest to the apical (outer) surface are not flattened but cuboidal.
In this specimen from the renal pelvis, the connective tissue immediately beneath the epithelium is inconspicuous, obscured by a layer of smooth muscle (note elongated nuclei). Beneath the smooth muscle is loose connective tissue, including conspicuous adipocytes (the clear round "bubbles").
Comments and questions: dgking@siu.edu
SIUC / School
of Medicine / Anatomy / David
King
https://histology.siu.edu/intro/RE022c.htm
Last updated: 8 June 2022 / dgk