

Notes
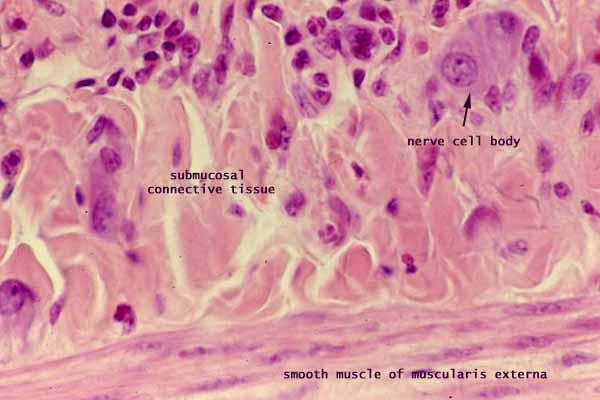
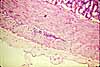
The submucosa consists of loose, fibrous connective tissue which facilitates motility of the GI tract by permitting the mucosa to move flexibly during peristalsis.
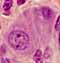
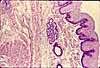
Within the submucosa lies Meissner's plexus (the name commemorates Georg Meissner, b. 1829), also called the submucosal plexus, a network of parasympathetic nerve fibers and cell bodies which influence smooth muscle of the muscularis mucosae.
Nerve cell bodies are usually rather conspicuous. Each cell body can be quite large (up to ~50µm), with relatively basophilic cytoplasm and with a large, round, euchromatic nucleus with a single prominent nucleolus.
Related examples:
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
Comments and questions: dgking@siu.edu
SIUC / School
of Medicine / Anatomy / David
King
https://histology.siu.edu/erg/GI008b.htm
Last updated: 14 May 2022 / dgk