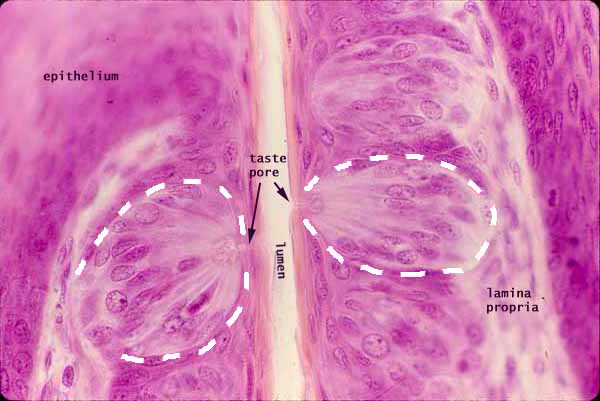


Taste buds on the human tongue are found on fungiform papilla and on a few large circumvallate papillae (located at the back of the tongue).
The image above was taken from rabbit tongue, where taste buds often face one another across a narrow cleft between adjacent foliate (leaf-shaped) papillae.
Although the arrangement of papillae differs between rabbit and human, the taste buds appear similar and are much easier to find on specimens of rabbit tongue. (Why this should be is unclear. Rabbits, which are well known for eating their own droppings, are hardly models for gourmet sensitivity.)
Each egg-shaped taste bud (white dashed outline) includes elongated sensory cells which extend across the thickness of the epithelium, from the lamina propria to the taste pore at the surface.
The elongated cells comprising a taste bud include both sensory cells and support (sustentacular) cells. Shorter cells with round nuclei at the basal end of the tastebud are stem cells.
Nerve fibers innervating the basal ends of the sensory cells are not visible on this specimen (click on diagram at right for a schematic view).
Related examples:
 |
 |
 |
Comments and questions: dgking@siu.edu
SIUC / School
of Medicine / Anatomy / David
King
https://histology.siu.edu/erg/GI048b.htm
Last updated: 29 July 2022 / dgk