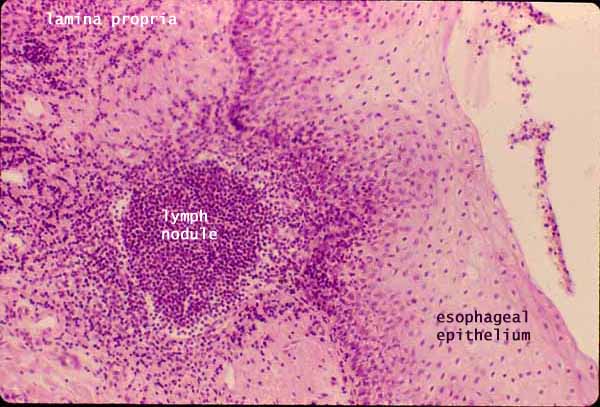

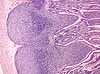
Esophagus, mucosa with lymph nodule

Notes
Aggregations of lymphocytes may occur anywhere along the GI tract, as here in the mucosa of the esophagus, near the esophagus-stomach junction.
A germinal center (the defining feature of a lymph nodule) is not visible here, but is probably nearby out of the plane of section.
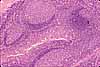
The tissue around a mucosal lymph nodule is usually filled with lymphocytes migrating to and from the germinal center. As in the image above, lymphocytes infiltrate not only lamina propria but also nearby epithelium. (In this image, most of the small deeply-stained dots surrounding the nodule are the nuclei of lymphocytes.)
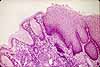
Lymph nodules may occur in lamina propria anywhere along the GI tract. At sites where lymph nodules characteristically occur in clusters (tonsils, Peyer's patches, appendix), the mass of lymphoid tissue may obscure the mucosa and intrude into the submucosa.
Inflammation can present a similar but less organized appearance of lymphocyte accumulation.
Related examples:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Comments and questions: dgking@siu.edu
SIUC / School
of Medicine / Anatomy / David
King
https://histology.siu.edu/erg/GI051b.htm
Last updated: 26 May 2022 / dgk