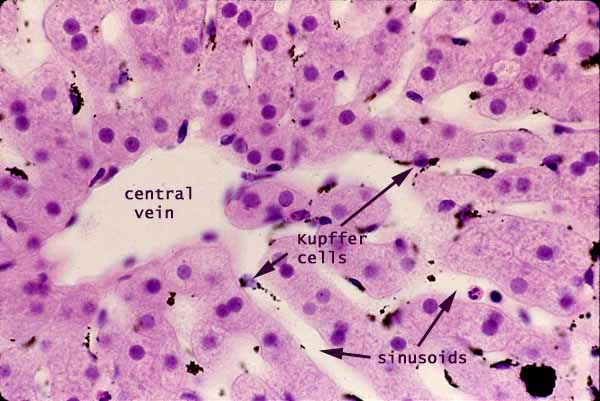

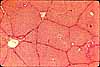
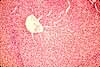
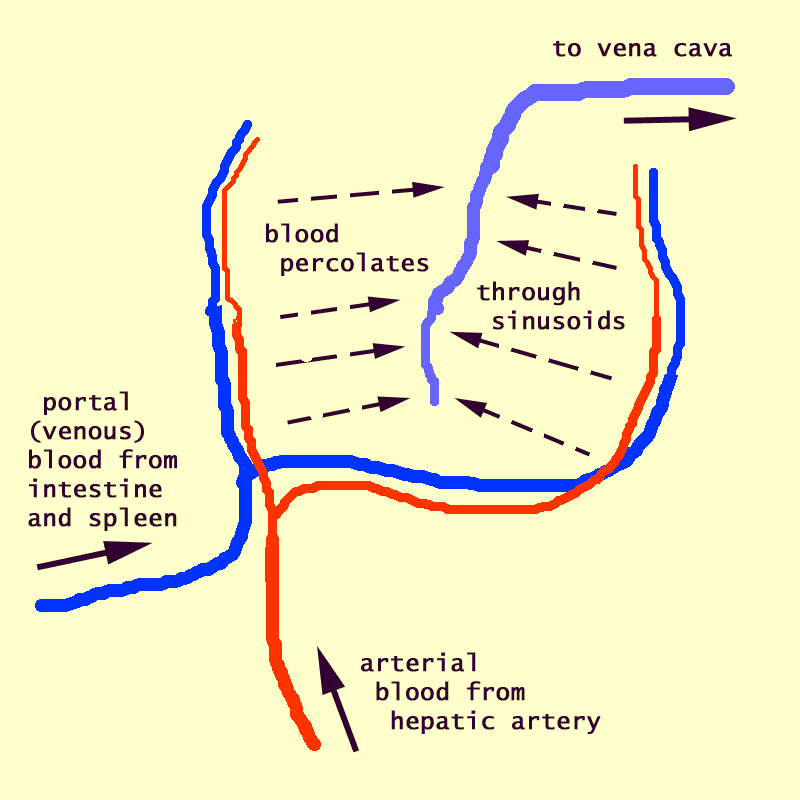
Liver, sinusoids with Kupffer cells

Notes
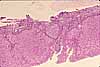
This specimen comes from an animal which was injected intravenously with a suspension of carbon particles. These particles are scavenged by macrophages, most notably by those in the liver which are called Kupffer cells, whose cytoplasm becomes packed with black carbon particles.
In the absence of such experimental demonstration, Kupffer cells can be recognized by their oval nuclei closely associated with sinusoidal spaces.
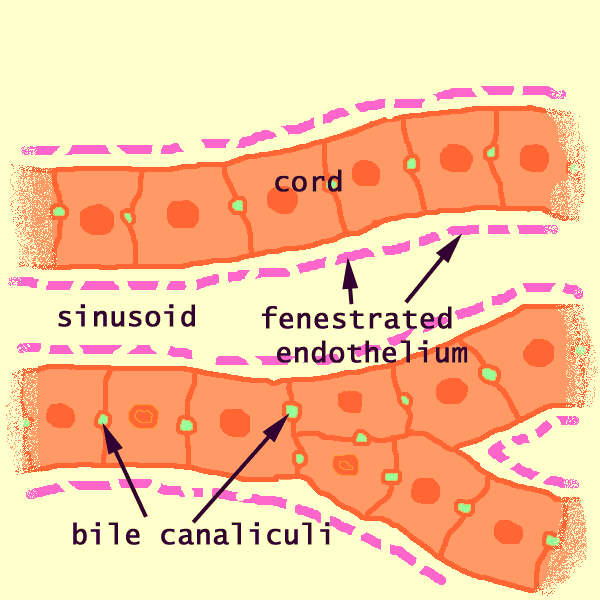
Endothelial cells appear similar, but with thinner (flatter) and denser nuclei and with less conspicuous cytoplasm.
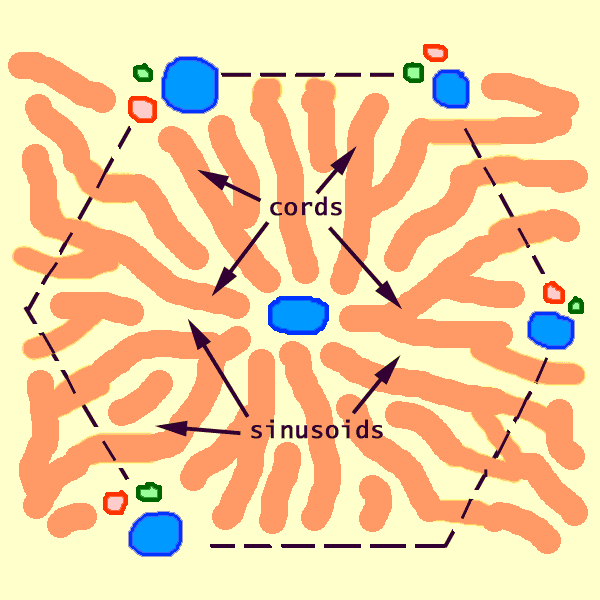
In contrast, the hepatocytes which comprise the hepatic cords have round nuclei surrounded by abundant cytoplasm.
The space of Disse is barely visible here and there on this image, appearing as a thin bright band between hepatocyte cytoplasm and the thinner, darker band which represents the endothelium (white arrow in image to right).
Related examples:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Comments and questions: dgking@siu.edu
SIUC / School
of Medicine / Anatomy / David
King
https://histology.siu.edu/erg/GI166b.htm
Last updated: 14 May 2022 / dgk