

Notes
Click on the image to identify the tissues. Depending on your browser, simply "hovering" over an area may produce a label.)
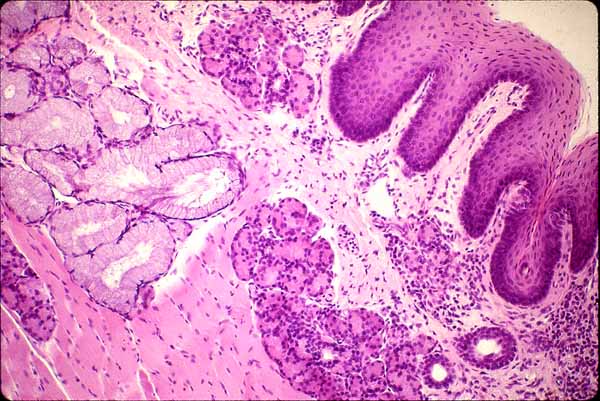
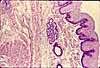
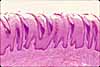
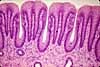
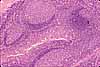
In this image of the lower surface of the tongue, the mucosa -- with its non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium and unspecialized lamina propria -- is fairly typical of the oral cavity in general (including cheek, lip and soft palate). Small serous and mucous glands are scattered thoroughout the lamina propria and submucosa. Deep to the submucosa of tongue, cheek, lip, and soft palate may be found striated muscle.
Note that the basal surface of the epithelium is deeply indented by connective tissue papillae of lamina propria.
In the oral cavity, there is not a clear distinction between lamina propria and submucosa. The boundary is indicated rather arbitrarily in this image.
Related examples:
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Comments and questions: dgking@siu.edu
SIUC / School
of Medicine / Anatomy / David
King
https://histology.siu.edu/erg/GI140b.htm
Last updated: 17 May 2022 / dgk