

Notes
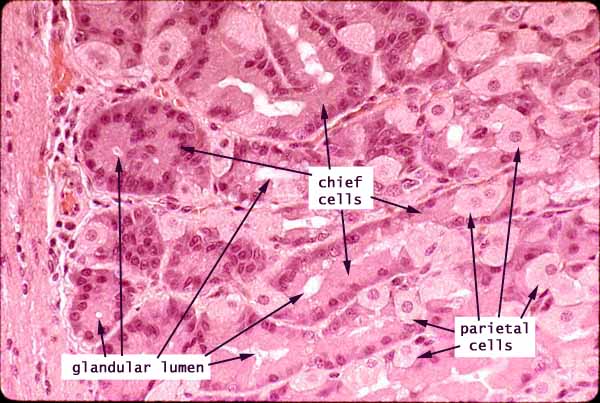
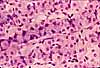
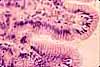
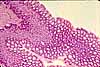
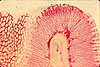
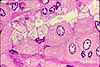
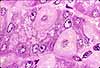
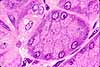
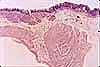
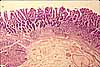
Most of the bulk of the gastric mucosa is occupied by secretory cells of the gastric glands, primarily parietal cells and chief cells, together with lamina propria.
In routine sections, the secretory cells often appear rather jumbled together. Sometimes, however, tubular organization is more evident, especially deep in the gastric glands near the muscularis mucosae, as in the figure above.
Cells with conspicuous eosinophilic cytoplasm and centrally located nuclei (sometimes paired) are the acid-secreting parietal cells.
Cells with basal nuclei, basally basophilic cytoplasm, and apical vesicles are the enzyme-secreting chief cells.
The glands are separated by thinner strands of lamina propria, visible as strands of denser, flattened or irregular nuclei.
Related examples:
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Comments and questions: dgking@siu.edu
SIUC / School
of Medicine / Anatomy / David
King
https://histology.siu.edu/erg/GI178b.htm
Last updated: 27 May 2022 / dgk